TRACHOMA: THE DISEASE
- June 7th, 2010
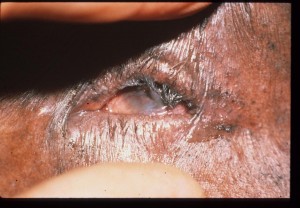
Trachoma is a bacterial eye infection that is passed from person to person through direct contact. It thrives in dry conditions where overcrowded housing and unhygienic conditions prevail. What begins as an infection under the eyelid soon causes scaring, and with repeat infection, the eyelashes turn in and scratch the eye causing extreme discomfort and eventually irreversible blindness. In the early stages it can be treated with basic antibiotics, but requires surgery as the disease becomes more advanced. Preventing trachoma requires little more than basic hygiene and facial cleanliness.
The SAFE strategy, designed by The World Health Organisation (WHO), incorporates the four major elements needed to eradicate trachoma – Surgery, Antibiotics, Facial cleanliness and Environmental improvement.